이 블로그 검색
2015년 11월 5일 목요일
2015년 10월 26일 월요일
Haskell Package 지우기
하스켈을 하다보면 패키지 이름이 겹치는 경우가 있다. 그럴경우 사용하지 않는 한가지를 아래와 같이 처리한다.
ghc-pkg unregister --force 패키지이름
ex) ghc-pkg unregister --force regex-compat-0.95.1Haskell - Not in scope: 'pure'
ghci> :t pure
<interactive>:1:1: Not in scope: ‘pure’
ghci> :m +Control.Applicative
ghci> :t pure
pure :: Applicative f => a -> f a2015년 10월 19일 월요일
Blender tip #30: Changing Modifier Settings on Multiple Objects at Once
Sometimes, when you’re working on a scene that has lots of different objects with modifiers on it, you might want to change a specific modifier setting on several objects at once (like the Subdivision Surface modifier for instance). Luckily, Blender has a cool little feature that enables you to do just that.
(A) Select all the objects with the same Modifier that you want to change.
(B) Go to the modifiers panel and locate the modifier (in this case the Subdivision Surface modifier).
(C) Simply hold down the ALT key while changing any value, and the changes will be assigned to all of the other selected objects that have the same modifier.
2015년 9월 22일 화요일
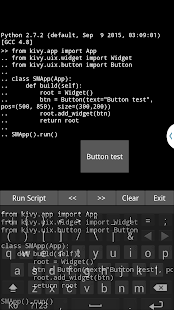
Python Interpreter For Android - REPL
Link : https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=enurisoft.com.pythoninterpreter
 Python Interpreter For Android
Python Interpreter For Android
It is Python interpreter for Android.
It is Python REPL.
It offers a great learning experience for Python beginners.
It is written in python using the Kivy framework. (http://kivy.org)

It is Python interpreter for Android.
It is Python REPL.
It offers a great learning experience for Python beginners.
It is written in python using the Kivy framework. (http://kivy.org)
2015년 9월 9일 수요일
Kivy - Buildozer 각종 오류 해결하기
1. kivy 1.9.0 버전을 buildozer로 apk를 만들경우 몇가지 버전을 맞추어주어야 한다.
cython 0.21
android build tool revision 22.0
pygments 설치
ant 1.9.3
2. buildozer.spec 파일에 pygments와 같은 추가 모듈이 있는 경우 available module 목록에 없다며 에러를 뱉어내는 경우가 있다.
아래와 같이 python 가상환경을 실행후 buildozer android debug or release를 다시 실행해주면 빌드가 된다.
virtualenv --python=python2.7 ./venv
cython 0.21
android build tool revision 22.0
pygments 설치
ant 1.9.3
2. buildozer.spec 파일에 pygments와 같은 추가 모듈이 있는 경우 available module 목록에 없다며 에러를 뱉어내는 경우가 있다.
아래와 같이 python 가상환경을 실행후 buildozer android debug or release를 다시 실행해주면 빌드가 된다.
virtualenv --python=python2.7 ./venv
2015년 9월 8일 화요일
Kivy - Buildozer로 Android APK 만들기
가장먼저 buildozer install하기
인스톨이 완료되면 초기화를 실행한다.
git clone https://github.com/kivy/buildozer.git cd buildozer sudo python2.7 setup.py install
인스톨이 완료되면 초기화를 실행한다.
buildozer init
init를 완료하고 나면 buildozer.spec 파일이 생성되는데 정보를 적절하게 입력해준다.
[app]
# (str) Title of your application
title = Kivy Python Interpreter
# (str) Package name
package.name = KivyPythonInterpreter
# (str) Package domain (needed for android/ios packaging)
package.domain = enurisoft.com
# (str) Source code where the main.py live
source.dir = /home/mataeoh/Work/PythonProject/Kivy/ScrollBar
# (list) Source files to include (let empty to include all the files)
source.include_exts = ttf,py,png,jpg,atlas,kv
# (list) Source files to exclude (let empty to not exclude anything)
#source.exclude_exts = spec
# (list) List of directory to exclude (let empty to not exclude anything)
#source.exclude_dirs = tests, bin
# (list) List of exclusions using pattern matching
#source.exclude_patterns = license,images/*/*.jpg
# (str) Application versioning (method 1)
#version.regex = __version__ = '(.*)'
#version.filename = %(source.dir)s/main.py
# (str) Application versioning (method 2)
version = 1.2.0
# (list) Application requirements
# comma seperated e.g. requirements = sqlite3,kivy
requirements = kivy
# (str) Custom source folders for requirements
# Sets custom source for any requirements with recipes
# requirements.source.kivy = ../../kivy
# (list) Garden requirements
#garden_requirements =
# (str) Presplash of the application
#presplash.filename = %(source.dir)s/data/presplash.png
# (str) Icon of the application
#icon.filename = %(source.dir)s/icon/kivy-icon-128.png
# (str) Supported orientation (one of landscape, portrait or all)
orientation = portrait
# (bool) Indicate if the application should be fullscreen or not
fullscreen = 1
#
# Android specific
#
# (list) Permissions
#android.permissions = INTERNET
# (int) Android API to use
#android.api = 14
# (int) Minimum API required (8 = Android 2.2 devices)
#android.minapi = 8
# (int) Android SDK version to use
#android.sdk = 21
# (str) Android NDK version to use
#android.ndk = 9c
# (bool) Use --private data storage (True) or --dir public storage (False)
#android.private_storage = True
# (str) Android NDK directory (if empty, it will be automatically downloaded.)
#android.ndk_path =
# (str) Android SDK directory (if empty, it will be automatically downloaded.)
#android.sdk_path =
# (str) python-for-android git clone directory (if empty, it will be automatically cloned from github)
#android.p4a_dir =
# (list) python-for-android whitelist
#android.p4a_whitelist =
# (str) Android entry point, default is ok for Kivy-based app
#android.entrypoint = org.renpy.android.PythonActivity
# (list) List of Java .jar files to add to the libs so that pyjnius can access
# their classes. Don't add jars that you do not need, since extra jars can slow
# down the build process. Allows wildcards matching, for example:
# OUYA-ODK/libs/*.jar
#android.add_jars = foo.jar,bar.jar,path/to/more/*.jar
# (list) List of Java files to add to the android project (can be java or a
# directory containing the files)
#android.add_src =
# (str) python-for-android branch to use, if not master, useful to try
# not yet merged features.
#android.branch = master
# (str) OUYA Console category. Should be one of GAME or APP
# If you leave this blank, OUYA support will not be enabled
#android.ouya.category = GAME
# (str) Filename of OUYA Console icon. It must be a 732x412 png image.
#android.ouya.icon.filename = %(source.dir)s/data/ouya_icon.png
# (str) XML file to include as an intent filters in <activity> tag
#android.manifest.intent_filters =
# (list) Android additionnal libraries to copy into libs/armeabi
#android.add_libs_armeabi = libs/android/*.so
#android.add_libs_armeabi_v7a = libs/android-v7/*.so
#android.add_libs_x86 = libs/android-x86/*.so
#android.add_libs_mips = libs/android-mips/*.so
# (bool) Indicate whether the screen should stay on
# Don't forget to add the WAKE_LOCK permission if you set this to True
#android.wakelock = False
# (list) Android application meta-data to set (key=value format)
#android.meta_data =
# (list) Android library project to add (will be added in the
# project.properties automatically.)
#android.library_references =
#
# iOS specific
#
# (str) Name of the certificate to use for signing the debug version
# Get a list of available identities: buildozer ios list_identities
#ios.codesign.debug = "iPhone Developer: <lastname> <firstname> (<hexstring>)"
# (str) Name of the certificate to use for signing the release version
#ios.codesign.release = %(ios.codesign.debug)s
[buildozer]
# (int) Log level (0 = error only, 1 = info, 2 = debug (with command output))
log_level = 2
# (int) Display warning if buildozer is run as root (0 = False, 1 = True)
warn_on_root = 1
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# List as sections
#
# You can define all the "list" as [section:key].
# Each line will be considered as a option to the list.
# Let's take [app] / source.exclude_patterns.
# Instead of doing:
#
#[app]
#source.exclude_patterns = license,data/audio/*.wav,data/images/original/*
#
# This can be translated into:
#
#[app:source.exclude_patterns]
#license
#data/audio/*.wav
#data/images/original/*
#
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Profiles
#
# You can extend section / key with a profile
# For example, you want to deploy a demo version of your application without
# HD content. You could first change the title to add "(demo)" in the name
# and extend the excluded directories to remove the HD content.
#
#[app@demo]
#title = My Application (demo)
#
#[app:source.exclude_patterns@demo]
#images/hd/*
#
# Then, invoke the command line with the "demo" profile:
#
#buildozer --profile demo android debug
디버그로 APK 빌드하기
buildozer android debug
릴리즈로 빌드하기
buildozer android release
Instructions for creating a signed, release APK, suitable for the Google Play Store
Fields
- my-project - The directory for your project
- my-new-key - The name of the key you generate
- my-alias - A short alias name for the key
- MyProject - The name of your project, and APK
- version - The version of this APK (not Kivy version)
Commands
$ cd ~
$ keytool -genkey -v -keystore ./keystores/<my-new-key>.keystore -alias <my-alias> -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -validity 10000
$ cd ~/<my-project>
$ source venv/bin/activate
$ buildozer android release
$ cd ~
$ jarsigner -verbose -sigalg SHA1withRSA -digestalg SHA1 -keystore ./keystores/<my-new-key>.keystore ./<my-project>/bin/<MyProject>-<version>-release-unsigned.apk <my-alias>
$ <key-password>
$ ~/.buildozer/android/platform/android-sdk-21/build-tools/22.0.1/zipalign -v 4 ./<my-project>/bin/<MyProject>-<version>-release-unsigned.apk ./<my-project>/bin/<MyProject>.apk
빌드도중 에러발생시
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "build.py", line 507, in
make_package(args)
File "build.py", line 356, in make_package
subprocess.check_call([ANT, arg])
File "/usr/lib/python2.7/subprocess.py", line 540, in check_call
raise CalledProcessError(retcode, cmd)
subprocess.CalledProcessError: Command '['ant', 'debug']' returned non-zero exit status 1
File "build.py", line 507, in
make_package(args)
File "build.py", line 356, in make_package
subprocess.check_call([ANT, arg])
File "/usr/lib/python2.7/subprocess.py", line 540, in check_call
raise CalledProcessError(retcode, cmd)
subprocess.CalledProcessError: Command '['ant', 'debug']' returned non-zero exit status 1
Android SDK Build-tools를 revision 20으로 다운을 받고 완료되면 buildozer를 재실행한다.
- Run
~/.buildozer/android/platform/android-sdk-21/tools/androidto launch the Android SDK Manager. - Click the
Deselect Alllink at the bottom of the window, and check the box next to "Android SDK Build-tools -- 20".
- Click the
Install 1 package...button. - Click
Accept Licenseand then click theInstallbutton.
피드 구독하기:
글 (Atom)

